Integrated development environment#
Python scripts are essentially text files. You could use any basic text editor such as Notepad or Notepad++ to write them. For instance, you could create a simple text file hello.py:
print("Hello World")
Then, you can use Python to execute it:
python hello.py
While this workflow is entirely functional, developers have created tools to facilitate script development and data exploration. These tools are known as Integrated Development Environments (IDEs). IDEs are applications that provide comprehensive facilities for coding. They often include features like syntax highlighting, autocompletion, and debugging tools, which can significantly enhance productivity and code quality. Moreover, many modern IDEs allow you to run your code interactively within the IDE itself, further enhancing the development and data exploration experience.
Spyder#

Spyder is a free and open-source scientific environment for Python, which is also written in Python. It is designed to meet the needs of scientists, engineers, and data analysts when working with Python. Its graphical interface has many similarities with MATLAB, making it an excellent choice for those transitioning from MATLAB to Python. However, for others, there might be alternative tools that offer more features.
I recommended to install Spyder in each conda environment using pip. This ensures that Spyder is configured to work within your current environment:
pip install spyder
To start Spyder, simply type:
spyder
Jupyter Notebook / JupyterLab#
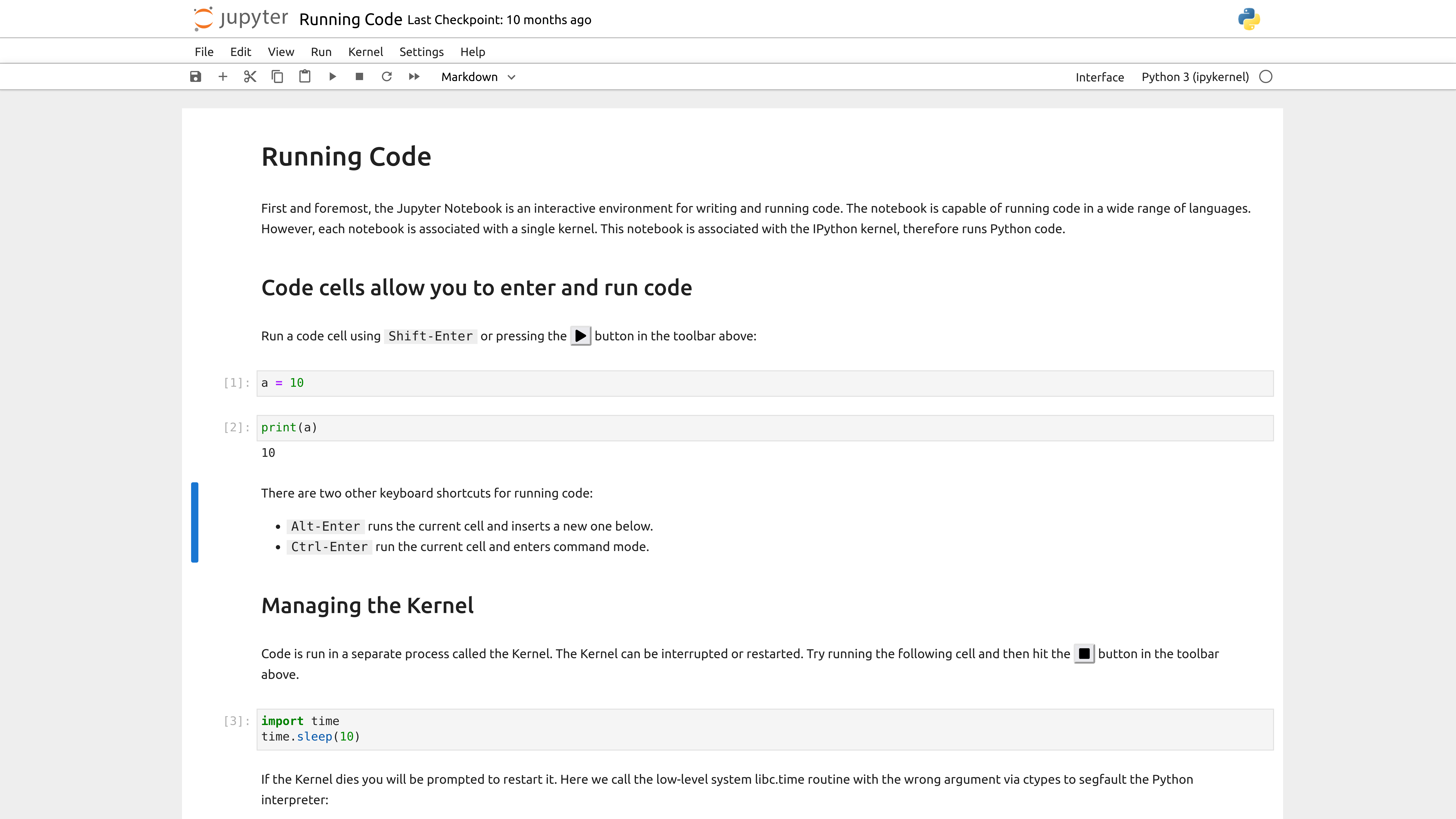
Jupyter Notebook and JupyterLab are powerful, interactive coding environments that facilitate data analysis and visualization. They operate as server-client applications. When you start a Jupyter server, a webpage is opened in your default web browser, allowing you to interact with interactive Python notebooks (.ipynb). These interfaces offer two main benefits:
Interactive Execution: Code is written in cells, which can be executed independently while retaining the state of the entire session. This allows for interactive experimentation without needing to rerun the entire script.
Rich Media Integration: Embed text (Markdown), plots, images, videos, and other rich media directly into the notebook. This feature is especially useful for documenting data analysis workflows and sharing results.
JupyterLab is an enhanced interface for Jupyter Notebooks, offering additional features like an integrated file browser and support for multiple panels. While it can be more handy and versatile, it retains all the core functionalities of Jupyter Notebook.
Usage#
To install Jupyter Notebook, use pip in your current conda environment:
pip install jupyter
To start Jupyter Notebook, run:
jupyter notebook
For JupyterLab, install it using:
pip install jupyterlab
and run it using:
jupyter lab
Note
Because Jupyter Notebook and JupyterLab are server-client applications, they can be easily integrated into web platforms. Instead of running the Jupyter server on your own computer, the server can be run on a remote machine. This feature is utilized by several cloud services, such as:
Google Colab: An online Jupyter Notebook environment hosted by Google, which allows you to write and execute Python code in your browser with zero configuration required. Google Colab
Binder: A service that lets you create sharable, interactive computing environments from GitHub repositories. It enables you to run Jupyter Notebooks without needing to install any software locally. Binder
This feature can also be used to run code on another computer within your network and/or a virtual machine on your own computer (docker/ Windows subsystem for Linux (WSL))
Additionally, you can access powerful computational resources by starting a Jupyter server on the High-Performance Computing (HPC) cluster. This is particularly useful for running resource-intensive analyses that wouldn’t run efficiently on your personal computer. For more details on how to use Jupyter servers on HPC, check this link: Using Jupyter on HPC
Visual Studio Code (VS Code)#
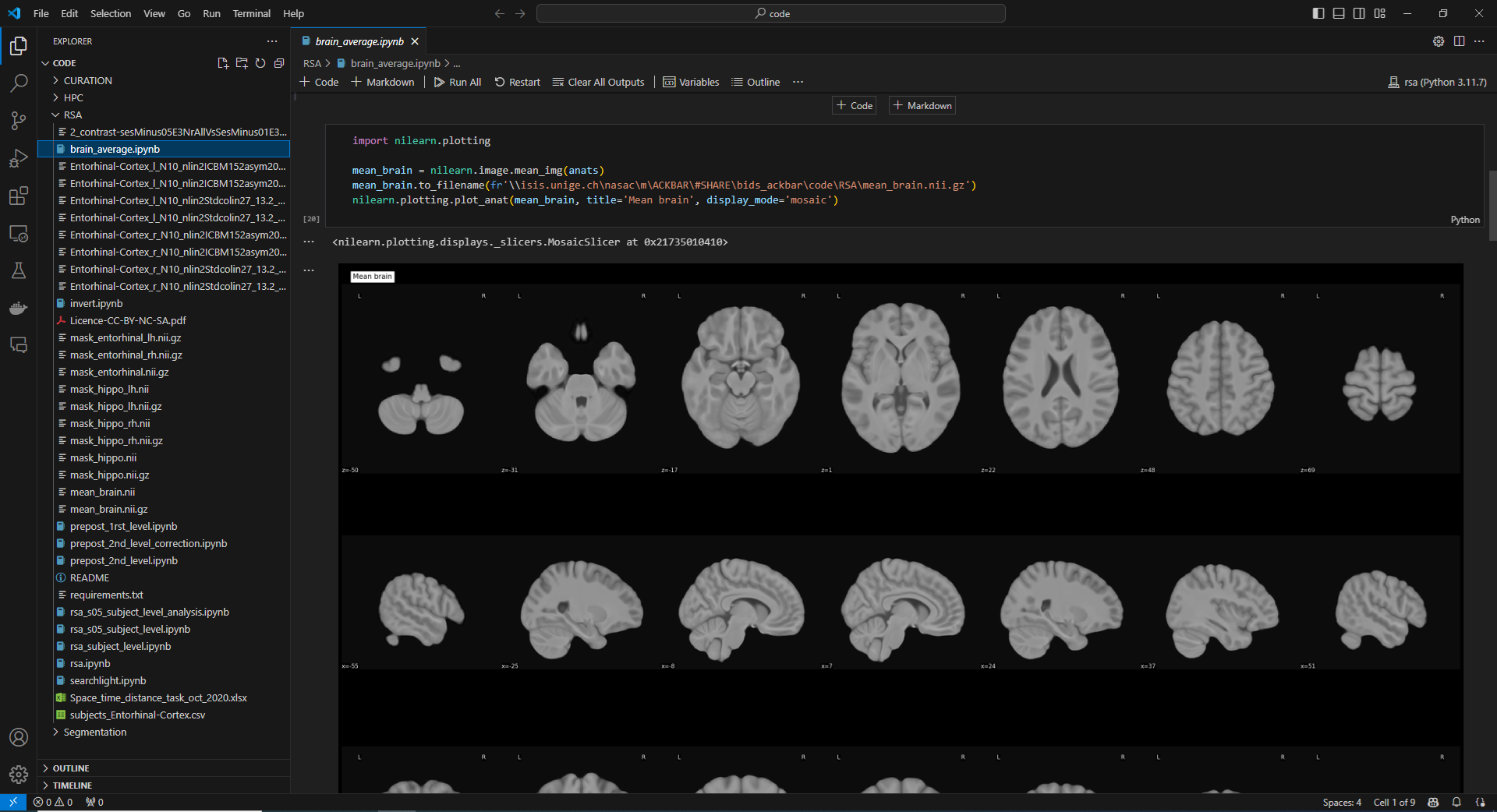
Visual Studio Code (VS Code) is an IDE developed by Microsoft. It is an excellent choice for Python development but also supports many other programming languages, making it a highly versatile tool for a wide range of coding needs.
Jupyter Notebooks Integration: VS Code can edit both classic Python scripts and Jupyter Notebooks. When you open a .ipynb file, it automatically starts a Jupyter server for you or connects to an existing one, providing a seamless experience for notebook users.
Multi-language Support: VS Code is not limited to Python. It supports numerous programming languages such as JavaScript, C++, Java, and more, through its extensive marketplace of extensions.
Marketplace Extensions: The VS Code marketplace allows you to install extensions tailored to your specific needs. Whether you need tools for debugging, version control, or integrating cloud services, there is an extension available.
Jupyter Notebooks Integration: VS Code can edit both classic Python scripts and Jupyter Notebooks. When you open a
.ipynbfile, it automatically starts a Jupyter server for you or connects to an existing one, providing a seamless experience for notebook users.
As VScode is developed by Microsoft, it integrates exceptionally well with other Microsoft tools:
GitHub Integration: VS Code has built-in support for Git and GitHub, allowing you to manage your repositories directly within the IDE. You can commit changes, push to repositories, and review pull requests seamlessly.
GitHub Copilot: Students and educators can access GitHub Copilot, an AI-powered code completion tool that provides “Chat GPT in the IDE” experience. Copilot assists you by suggesting whole lines or blocks of code as you type, significantly enhancing productivity.
Getting Started#
To start using VS Code for Python and Jupyter Notebooks:
Download and Install: Download VS Code from the official website.
Install Extensions: Install the Python extension and Jupyter extension from the VS Code marketplace.
Open or Create Projects: Open your Python scripts or Jupyter Notebooks directly in VS Code. For Jupyter Notebooks, the server will start automatically or connect to an existing one.
Make sure to install ipykernel in each environment you want to use with VS code
pip install ipykernel
Note
VS Code is also a server-client application and can be integrated into web platforms. GitHub Codespaces (features/codespaces) allows you to start a VS Code server and access it from your web browser.
As with Jupyter Notebooks, a VS Code server can also be started on another computer within your network, a virtual machine on your own computer (Docker/Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)), and the UNIGE HPC.